With Builder's Upload API, developers can programmatically upload files such as images, PDFs, and videos.
Developers can use the Upload API to automate the asset upload process, saving time and reducing manual effort.
- Create a Private API Key in your Organization Account Settings.
- Review Managing Private API Keys to keep your key secure. Note that only those with Developer or Admin permissions can create Private API Keys.
The endpoint supports the following query parameters:
&name: specifies the name of the uploaded file.&altText: provides alternative text for accessibility and SEO.&title: sets a default title for the uploaded asset.&folder: uploads the file to a specific folder in the Asset Library using the folder ID.&url: uploads a file from a hosted URL instead of directly uploading the file content.
https://builder.io/api/v1/upload?name={ASSET_NAME}&altText={ASSET_ALT_TEXT}&title={ASSET_TITLE}&folder={ASSET_FOLDER_ID}To upload a file, replace the following placeholders in the API request with the actual filename, alt text, title, and folder ID:
ASSET_NAMEASSET_ALT_TEXTASSET_TITLEASSET_FOLDER_ID
- Copy your Private API Key.
- Make a
POSTrequest to the endpoint with the filename as a parameter for your file. AddaltTextandtitlefor accessibility. - Provide the path in the request body. The file must be under 100 MB.
- Include the Authorization header with your Private API Key.
- Specify the file type in the
Content-Typeheader.
A successful POST request returns a JSON response with the URL of the uploaded file.
To observe the file upload process, send curl request with name, altText, and title parameters, along with the following headers to upload an image:
--data-binaryin the request body to specify the file path.Authorizationheader with your Private API Key.Content-Typeheader to define the file MIME type.
curl "https://builder.io/api/v1/upload?name=ASSET_NAME&altText=ASSET_ALT_TEXT" \
-X POST \
--data-binary "@/path/to/your-file.extension" \
-H "Authorization: Bearer YOUR_PRIVATE_KEY" \
-H "Content-Type: image/png"
A successful upload returns a JSON response containing details about the uploaded file, including its URL.
{
"status": 200,
"message": "Success",
"url": "https://cdn.builder.io/api/v1/image/..."
}You can also set the name, alt text, and title for the files from the Asset library.
- Use the Node
fsmodule to read the file from disk with thefs.readFileSync(filePath)function. - Assign the resulting binary data of the file to a variable.
- Specify the upload URL with query parameters with
nameandaltText. - Use
fetch()to send aPOSTrequest to the endpoint, passing theURLas the first parameter and therequestObjectas the second parameter. - Set the method type to
POSTand include theAuthorizationandContent-Typeheaders in the object. - Parse the JSON from the
fetch()request and output the console.
// Import required modules
const fetch = require("node-fetch");
const fs = require("fs");
/**
* Upload an image file to Builder's Asset Library using Upload API
* @param {string} filePath - The path to the image file.
*/
async function uploadImage(filePath) {
try {
// Read the file as binary data
const fileData = fs.readFileSync(filePath);
// Define the API endpoint with parameters for file name and alt text
const url = "https://builder.io/api/v1/upload?name=ASSET_NAME&altText=ASSET_ALT_TEXT";
// Send a POST request to upload the file
const response = await fetch(url, {
method: "POST",
body: fileData, // Attach the binary file data
headers: {
"Authorization": "Bearer YOUR_PRIVATE_API_KEY", // Replace with your Builder private API key
"Content-Type": "image/jpg", // examples: "image/png" or "application/pdf"
},
});
// Parse the JSON response
const data = await response.json();
// Log the uploaded file URL or any response details
console.log("Upload successful:", data);
return data; // Return the response for further use if needed
} catch (error) {
console.error("Upload failed:", error);
}
}
// Example usage: Upload an image
uploadImage("./path-to-media/<filename>.ext");
- Use an
<input>tag to upload the file. Assign the binary data of the selected file to a variable. - Create a
Headers()object and add theAuthorizationtoken andContent-Typeto the headers. - Define
requestOptionswith thePOSTmethod,headers, andbodycontaining the file data. - Send a
fetch()request withrequestOptionsto the upload endpoint as anURL. - Convert the resolved response from the
fetch()request totext. - Log the response to the console.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<body>
<script>
// Handle file upload when button is clicked
document.getElementById('uploadBtn').addEventListener('click', () => {
const fileInput = document.getElementById('pdfInput');
if (!fileInput.files || !fileInput.files[0]) {
return alert("Please select a PDF file.");
}
const pdfFile = fileInput.files[0]; // file in binary data
// Create Headers() object
const myHeaders = new Headers();
// append the authorization token to the headers object
myHeaders.append("Authorization", "Bearer builder-private-key");
// append the content type to the headers object
myHeaders.append("Content-Type", "application/pdf");
// Define the fetch options.
const requestOptions = {
method: 'POST',
headers: myHeaders,
body: pdfFile,
redirect: 'follow'
};
// Endpoint URL.
const url = "https://builder.io/api/v1/upload?name=ASSET_NAME&altText=ASSET_ALT_TEXT";
fetch(url, requestOptions)
// parse the resoonse into plain text
.then(response => response.text())
.then(result => console.log("Upload successful:", result))
.catch(error => console.error("Error during upload:", error));
});
</script>
<input type="file" id="pdfInput" accept="application/pdf">
<button id="uploadBtn">Upload PDF</button>
</body>
</html>- Specify the upload URL with query parameters for url ,
nameandaltText. - Use
fetch()to send aPOSTrequest to the endpoint, passing theURLas the first parameter and therequestObjectas the second parameter. - Set the method type to
POSTand include theAuthorizationandContent-Typeheaders in the object. - Parse the JSON from the
fetch()request and output the console.
// Import required modules
const fetch = require("node-fetch");
/**
* Upload an image file to Builder's Asset Library using Upload API
* @param {string} fileUrl - The url of the remotely hosted image file.
*/
async function uploadImage(fileUrl) {
try {
// Define the API endpoint with query parameters for file name and alt text
const url = `https://builder.io/api/v1/upload?name=Builder-logo.png&url=${fileUrl}altText=Builder%20promo%20logo`;
// Send a POST request to upload the file
const response = await fetch(url, {
method: "POST",
body: fileData, // Attach the binary file data
headers: {
"Authorization": "Bearer YOUR_PRIVATE_API_KEY", // Replace with your Builder private API key
},
});
// Parse the JSON response
const data = await response.json();
// Log the uploaded file URL or any response details
console.log("Upload successful:", data);
return data; // Return the response for further use if needed
} catch (error) {
console.error("Upload failed:", error);
}
}
// Example usage: Upload an image
uploadImage("https://avatars.githubusercontent.com/u/35700027?s=200&v=4");

Tip: If you are using environments, you can manage folders only in the main environment. Builder syncs any updates made to folders in the main environment with child environments
To modify folders, use your main environment API Key.
For more information, visit Understanding Environments.
If you're using folders to organize assets in Builder, you can upload to a specific folder by adding the folder ID to the URL to the folder query parameter.
For example, to upload an asset to a folder with the ID abc123, add &folder=abc123 to the URL, replacing abc123 with your actual folder ID.
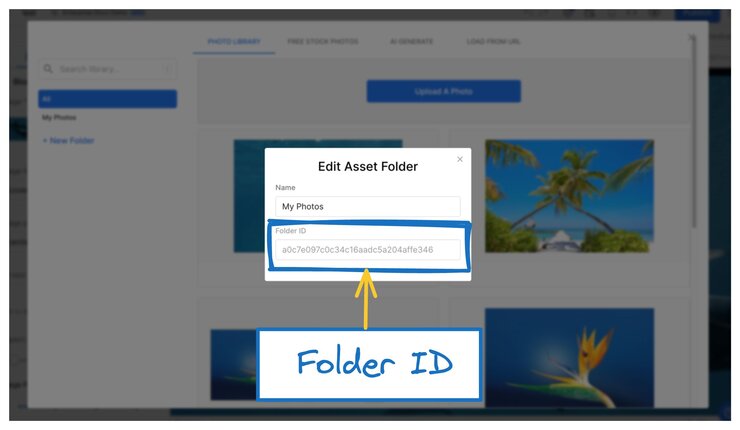
To find an asset folder ID:
- Go to the Asset Library.
- Hover over the folder and click the Pencil icon.
- In the dialogue that opens, copy the ID.
For example, if the ID were a0c7e097c0c34c16aadc5a204affe346, the syntax would be:
https://builder.io/api/v1/upload?name=MyFileName.pdf&folder=a0c7e097c0c34c16aadc5a204affe346The following image shows the Edit Asset Folder dialogue, with the folder ID highlighted: