



What Is Vibe Coding and How Does It Actually Work?
Most AI coding tools get you to a prototype fast, then die in compliance review or get rewritten by engineers who don't trust the output. That gap between hobbyist speed and production rigor is where vibe coding either becomes useful or stays a demo.
This guide explains what vibe coding actually is, how it works in practice, where it falls short, and what it takes to move from conversational prompts to mergeable code that survives enterprise standards.
What is vibe coding?
Vibe coding is an AI-assisted programming method where you describe what you want to build in plain English and AI generates the code. The term was popularized by AI researcher Andrej Karpathy in 2023. Instead of writing every line of syntax yourself, you communicate the “vibe” of what you want and let large language models handle the implementation details.
This is a full conversation where you describe entire features and refine them through dialogue. 84% of developers now use or plan to use these AI tools in their development process. You're still programming—the interface has just changed from typing code to having a conversation.
Practically, vibe coding means:
- Natural language as the interface: You describe what you want in everyday words, not programming syntax
- AI as the translator: Large language models convert your intent into working code based on patterns from millions of repositories
- Iterative refinement: Instead of debugging line by line, you tell the AI what's wrong and it fixes the code
- Focus on outcomes: You specify what should happen, not exactly how to implement it
Think of it as pair programming where your partner writes all the code while you focus on what the software should actually do.
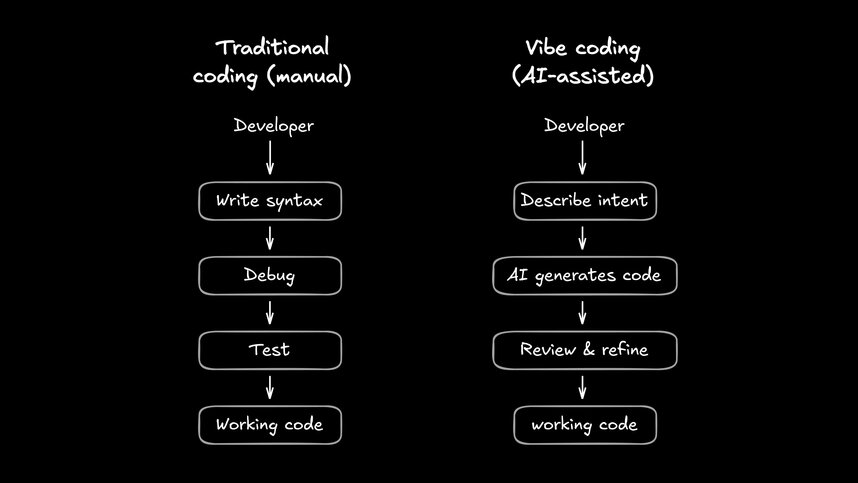
How does vibe coding work?
The workflow looks nothing like traditional development. You describe, the AI generates, you react, and the cycle repeats until the code matches your intent.
The conversational workflow
You start by describing what you want. This could be “create a login form with email validation” or “build a dashboard showing real-time sales data with filtering by region.” Developers using this approach complete tasks 55.8% faster than those writing code manually.
The AI gathers context from your codebase and constraints to generate an initial implementation. You review it, give feedback in plain language, and the AI adjusts until the code works as intended.
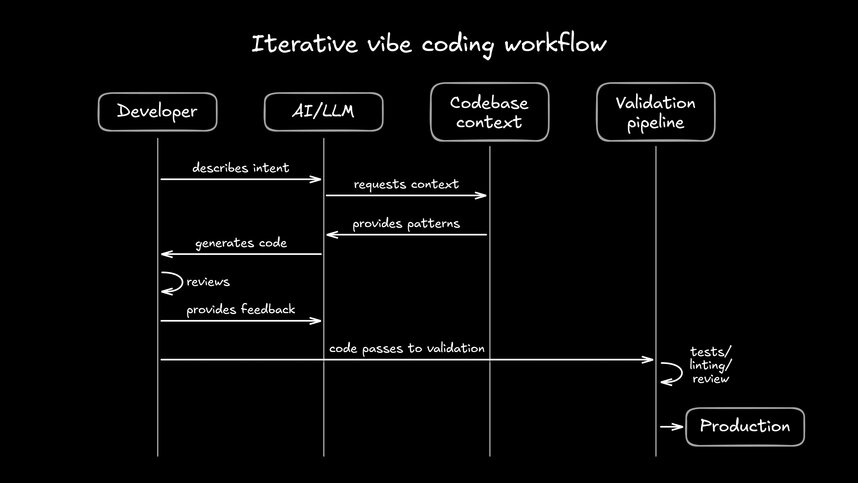
From prompt to working code
The technical pipeline involves several steps. Your natural language prompt gets processed by the LLM, which interprets your intent. The AI then synthesizes code matching both your description and patterns in your codebase.
Vague prompts produce vague code. The more context you provide, including your design system, coding standards, and existing patterns, the better the output. Generated code then flows through your normal validation: tests, linting, and code review before reaching production.
What tools enable vibe coding?
The ecosystem spans simple chat interfaces to full development environments. Each category serves different workflows and skill levels.
AI code completion assistants
Tools like GitHub Copilot work inside your existing IDE. They understand context from surrounding code and suggest completions as you type. Best for developers who want AI help without leaving their familiar environment.
Conversational AI coding tools
Chat-based tools like Claude, ChatGPT, and Gemini let you have extended conversations about code. Platforms like v0, Bolt.new, and Lovable go further by generating complete applications from prompts.
The tradeoff: ease of use versus production readiness. Most excel at prototypes but struggle with enterprise requirements like security reviews, existing codebases, and team standards.
Visual AI prototyping platforms
Some tools combine visual editing with vibe coding, letting you see changes while conversing with AI. Visual context helps AI understand intent better than text alone. This approach also works well for cross-functional teams where designers and PMs need to participate directly.

Why vibe coding matters for product teams
Vibe coding changes team dynamics, not just individual productivity. When anyone can express intent that becomes working code, the entire development process shifts.
- Faster prototyping: Move from idea to working UI in minutes instead of days
- Cross-functional contribution: PMs and designers participate directly in code creation
- Reduced translation loss: Intent stays intact from concept to implementation
- Rapid iteration: Test multiple approaches without manual rewrites each time
This is about giving everyone the ability to express intent that becomes real software. Engineers still own architecture and quality, but the translation bottleneck shrinks.
Real-world vibe coding use cases
Vibe coding excels at certain tasks and struggles with others. Knowing where it works helps you apply it wisely.
Strong use cases include:
- UI scaffolding: Generate component structures and layouts from descriptions
- CRUD operations: Build standard create, read, update, delete flows through conversation
- Test generation: Describe test scenarios and get working test suites
- Refactoring: Explain desired improvements in plain language and get cleaner code
- Documentation: Generate docs from code understanding
| Use Case | Traditional Approach | Vibe Coding Approach | Time Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
Feature scaffold | Manual component creation | Describe structure, get boilerplate | Hours to minutes |
Test coverage | Write each test case | Describe scenarios, generate tests | Days to hours |
Design implementation | Translate mockups manually | Describe design, get matching code | Weeks to days |
Where vibe coding falls short
Vibe coding has real limitations that matter for production software. Ignoring them creates technical debt and security risks.
Complex architecture decisions stay in human territory. AI generates code, but it cannot replace judgment about system design, performance tradeoffs, or long-term maintainability. While LLMs achieve 85.4% correctness on method-level tasks, they drop to just 37.0% correctness on complex class-level implementations. Generated code often needs manual tuning for performance-critical paths.
Determinism is another challenge. The same prompt might produce different outputs on different days. This makes reproducibility harder and requires careful version control of both prompts and outputs.
Security concerns also persist, as AI-generated code can introduce vulnerabilities that require human review to catch—only 55% of AI-generated code tested across major language models was found to be secure. Most AI tools are great for weekend projects, but almost none survive enterprise security reviews without significant oversight.
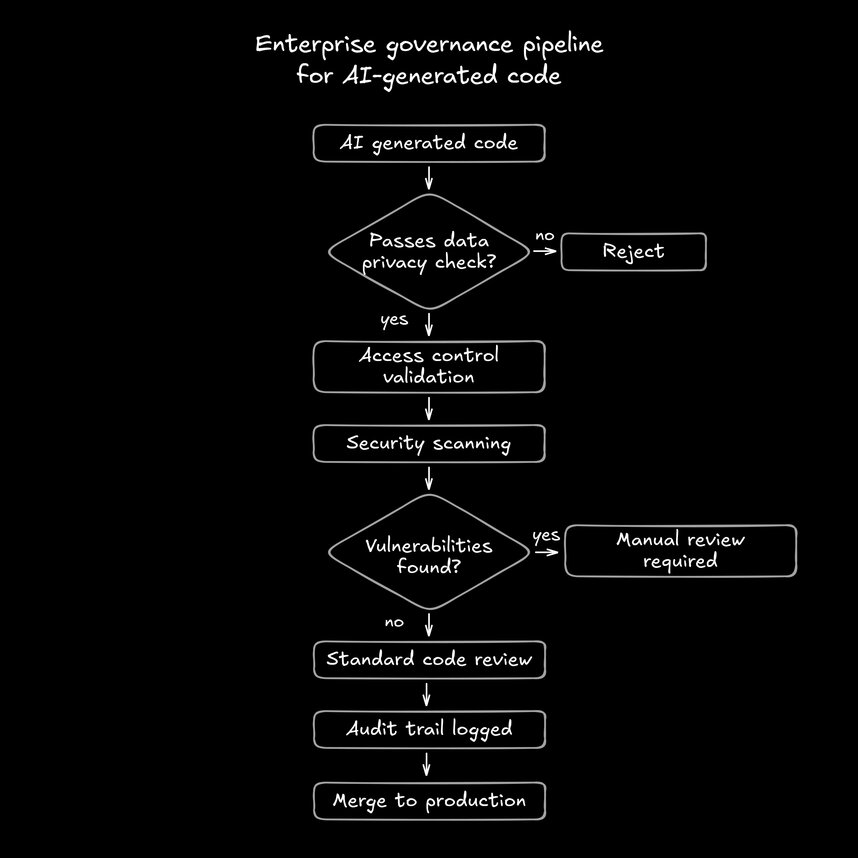
Security and governance considerations
Enterprise teams need more than fast code generation. They need controls, audit trails, and compliance.
Key areas to address:
- Data privacy: Ensuring prompts and code stay within organizational boundaries
- Access controls: Managing who can generate what types of code
- Audit trails: Tracking AI-generated changes for compliance
- Code scanning: Running generated code through security analysis before merge
A practical approach treats AI-generated code like any other contribution. It goes through standard review, must pass existing tests, and requires documentation of AI involvement. The speed benefit disappears if you skip the controls and spend weeks fixing security issues later.
How Builder.io enables production-ready vibe coding
Most vibe coding tools get you to a prototype. Few survive enterprise security reviews. That gap, between hobbyist speed and enterprise rigor, is exactly where Builder.io lives.
Builder.io connects directly to your repository and design system, so vibe coding happens in your actual codebase rather than an isolated sandbox. The AI uses your real components and tokens, producing code that matches existing patterns rather than improvising its own.
The workflow fits how teams actually build:
- Work inside your real system: Builder.io indexes your design system so prototypes speak your visual and technical language
- Use your team's actual data: Instead of placeholders, connect to real APIs and data sources from day one
- Edit visually, collaborate easily: PMs and designers preview and tweak layouts in the same environment engineers use
- Deliver code developers will merge: Each change lives as a small, reviewable diff with linters, type checks, and CI running as usual
The jump from "prototype" to "production" feels like normal iteration rather than a rebuild. That's the difference between vibe coding that ships and vibe coding that stays a demo.
If your team is tired of prototypes that die in compliance review, sign up for Builder.io and see vibe coding that actually makes it to production.
Common questions about vibe coding
What skills do you need to start vibe coding?
Basic programming understanding helps, but expertise is not required. The key skill is clearly describing what you want to build. If you can write a good user story or explain a feature to a teammate, you can vibe code.
Can vibe coding replace developers?
No. Vibe coding handles implementation details, but developers still own architecture, code quality, and system design. It amplifies productivity rather than replacing judgment.
How accurate is code generated through vibe coding?
Accuracy depends on context quality and prompt clarity. With good patterns and clear descriptions, modern LLMs produce usable code most of the time. Human review remains essential for catching edge cases and security issues.
What separates vibe coding from no-code platforms?
No-code tools abstract away code entirely using visual interfaces. Vibe coding generates actual code you can review, modify, and deploy through normal development workflows. You keep full control and visibility.

